class: middle, center # Lecture 2 ### 17 August 2020 Unit 3: **Functions**<br> Unit 4: **Types**<br> --- class: middle,center ### How CPU Executes a Program .fit[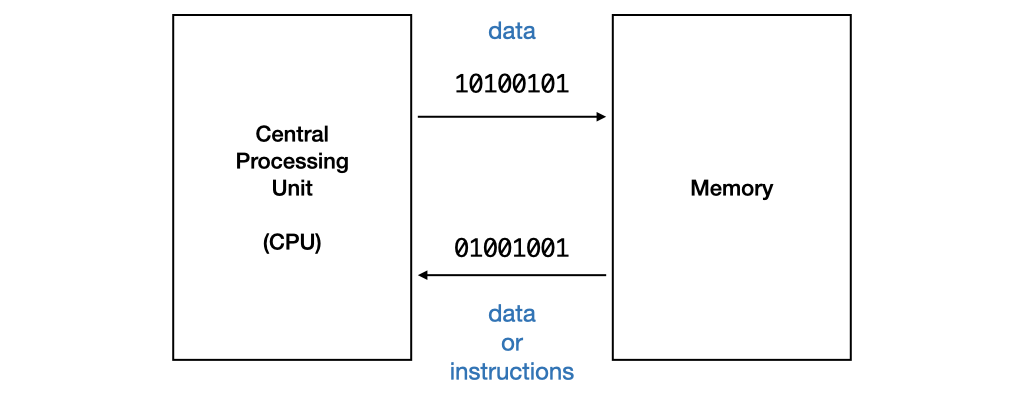] .tiny[(A highly simplfied view)] --- ### Compilation A compiler _compiles_ a program written in high-level language to machine code. .fit[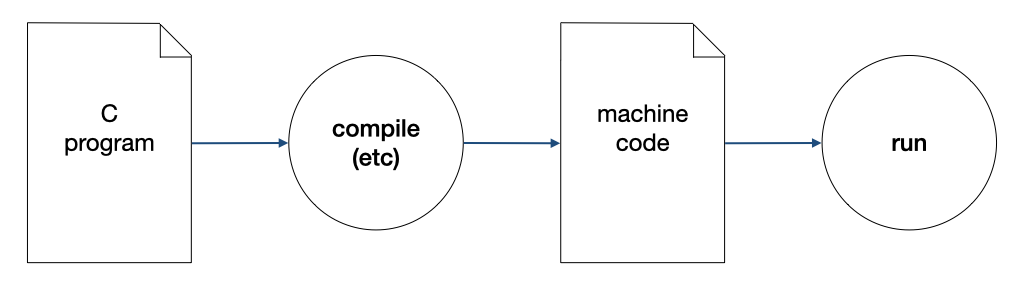] --- class: middle ### Learning to write a program that does what you want is the easy part. ### _Knowing what you want your program to do is the real challenge_! --- class: middle ### Computational problems are - problems that can be solved _step-by-step_ using an _algorithm_ by a computer - have _well-defined_ inputs, outputs, and constraints --- class: middle ## Flowchart .fit[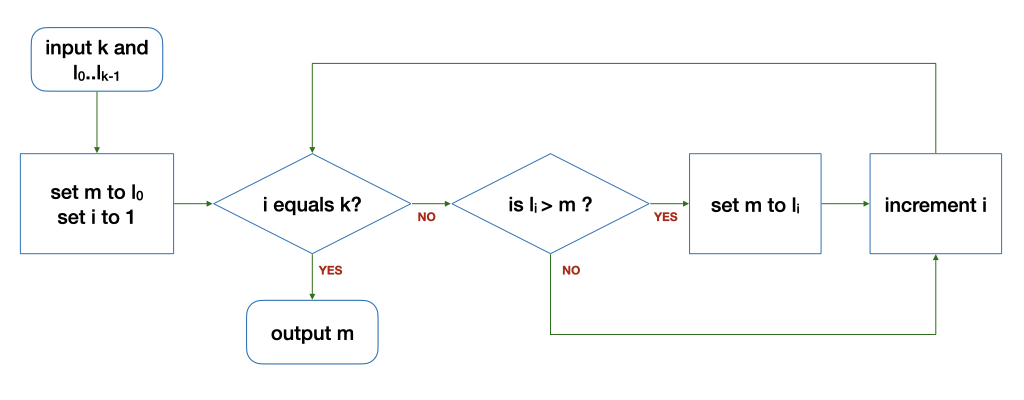] --- class: middle,center ## Functions --- class: middle,center .fit[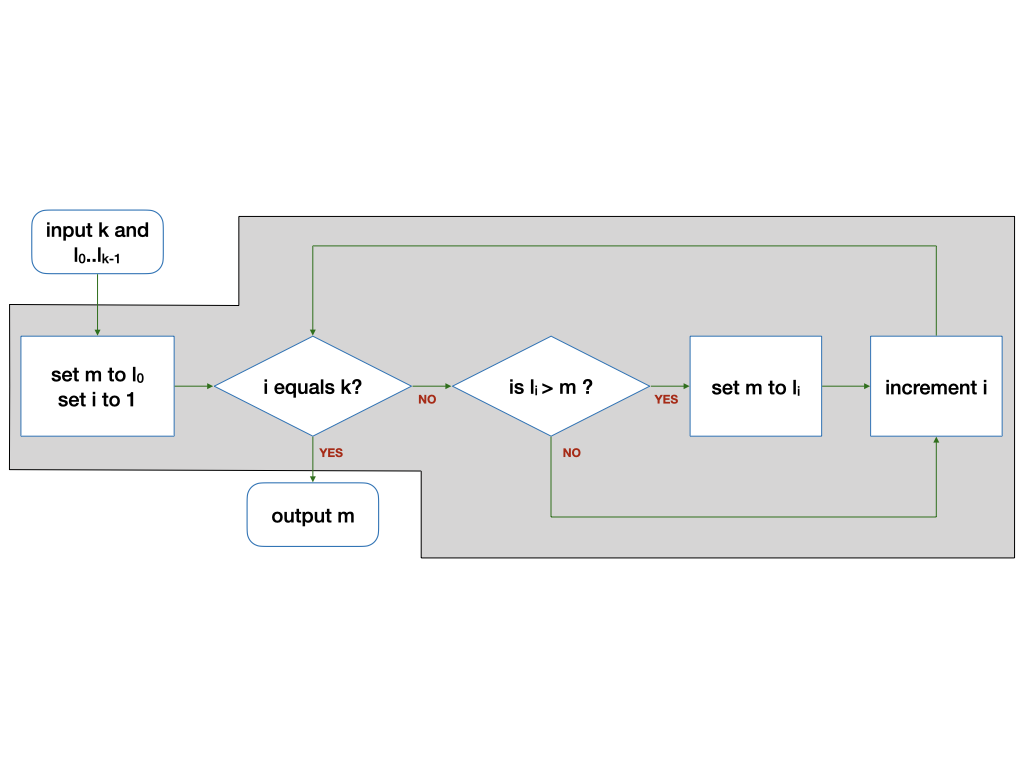] --- class: middle,center .fit[] --- ## Find The Range - The _range_ of a given list of $k$ integers is the difference between the max and the min values in the list. - Give an algorithm to find the range given a list $L$ of $k$ integers. --- class: middle,center ## $max(L, k) - min(L, k)$ --- class: middle,center ### Refer to a previous solution to a sub-problem, which we assume we already know how to solve. --- class: middle,center # "Wishful Thinking" --- class: middle ## "Wishful Thinking" - A powerful tool to help us think at a higher level. - We can focus on _what_ a function does, not _how_ it does it. --- class: middle,center ## A C program is just a collection of functions! --- class: middle ### A C program is just a collection of functions - written by you - provided by the standard C library - provided by other libraries --- class: middle ## Find The Mean - Give an algorithm to find the mean value given a list $L$ of $k$ integers. --- class: middle,center ## $\frac{sum(L,k)}{k}$ --- class:middle ## Find the Std Dev - Give an algorithm to find the standard deviation of a list $L$ of $k$ integers. $$\sqrt{\frac{\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2}{k}}$$ --- class:middle ## Let's break it down into sub-problems --- class: middle,center $$\sqrt{\frac{\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2}{k}}$$ --- class: middle,center $$\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2$$ set $\mu$ to $mean(L, k)$ set $L'$ to $subtract(L, k, \mu)$ set $L''$ to $square(L', k)$ set $total$ to $sum(L'', k)$ --- class: middle,center $$\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2$$ $sum(square(subtract(L,k,mean(L,k)),k),k)$ --- class: middle,center $$\frac{\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2}{k}$$ $mean(square(subtract(L,k,mean(L,k)),k),k)$ --- class: middle,center $$\sqrt\frac{\sum\_{i=0}^{k-1}(l\_i - \mu)^2}{k}$$ $sqrt(mean(square(subtract(L,k,mean(L,k)),k),k))$ --- class:middle ## "Wishful Thinking" - $square(L, k)$ - $subtract(L, k, \mu)$ - $sqrt(x)$ --- class:middle .fit[] --- class: middle,center ### Find the maximum among these numbers ``` 5 9 8 1 3 2 ``` --- class: middle,center ### Find the maximum among these numbers .tiny[ ``` 12 20 11 20 14 2 24 36 43 16 27 6 11 7 10 15 38 10 22 7 16 26 32 30 11 9 30 6 20 6 27 19 26 10 27 6 19 34 5 9 3 22 10 4 13 1 10 22 43 36 39 29 41 12 13 25 17 8 30 31 29 38 2 42 7 45 24 33 9 40 34 29 37 2 26 17 19 34 6 7 34 22 21 41 38 5 15 13 9 1 42 39 5 29 38 4 22 29 41 10 26 32 30 26 16 16 18 22 32 34 14 10 5 17 25 16 19 6 31 16 3 13 8 42 41 0 13 30 44 1 41 14 5 39 40 38 6 37 38 9 . ``` ] --- class: middle,center ### Compare the maximum among these numbers .tiny[ ``` 12 20 11 20 14 2 24 10 15 38 10 22 7 16 20 6 27 19 26 10 27 10 4 13 1 10 22 43 17 8 30 31 29 38 2 34 29 37 2 26 17 19 38 5 15 13 9 1 42 41 10 26 32 30 26 16 5 17 25 16 19 6 31 13 30 44 1 41 14 5 . ``` ] --- class: middle,center ### With the maximum among these numbers .tiny[ ``` 36 43 16 27 6 11 7 26 32 30 11 9 30 6 6 19 34 5 9 3 22 36 39 29 41 12 13 25 42 7 45 24 33 9 40 34 6 7 34 22 21 41 39 5 29 38 4 22 29 16 18 22 32 34 14 10 16 3 13 8 42 41 0 39 40 38 6 37 38 9 . ``` ] --- class: middle,center ### Compare `12` to the maximum among .tiny[ ``` 20 11 20 14 2 24 36 43 16 27 6 11 7 10 15 38 10 22 7 16 26 32 30 11 9 30 6 20 6 27 19 26 10 27 6 19 34 5 9 3 22 10 4 13 1 10 22 43 36 39 29 41 12 13 25 17 8 30 31 29 38 2 42 7 45 24 33 9 40 34 29 37 2 26 17 19 34 6 7 34 22 21 41 38 5 15 13 9 1 42 39 5 29 38 4 22 29 41 10 26 32 30 26 16 16 18 22 32 34 14 10 5 17 25 16 19 6 31 16 3 13 8 42 41 0 13 30 44 1 41 14 5 39 40 38 6 37 38 9 . ``` ] --- class: middle,center ## Wishful Thinking ### We know how to find $max(L,k)$ for smaller $k$ --- class: middle,center ### Let $max'(L, i, j)$ returns the maximum among $l\_i, l\_{i+1} \ldots l\_j$. --- class: middle,center ### $max(L,k)$ is the larger number between ### $max'(L, 0, \frac{k}{2}-1)$ and $max'(L, \frac{k}{2}, k-1)$ (for $k \ge 2$). --- class: middle,center ### $max'(L,0,k-1)$ is the larger between ### $max'(L, 0, \frac{k}{2}-1)$ and $max'(L, \frac{k}{2}, k-1)$ ($max'$ is calling itself!) --- class: middle,center ### Wishful thinking: Assuming we know how to solve $max'$ on a shorter list, we can solve $max'$ on a longer list! --- class: middle,center ### $max(L, k)$ is the larger number between ### $l\_0$ and $max'(L, 1, k-1)$ --- class: middle,center ### $max'(L, i, j)$ is the larger between ### $l\_i$ and $max'(L, i+1, j)$ if $i \not = j$. --- class: middle,center ### $max'(L, i, j)$ is just $l_i$ if $i$ equals $j$. --- class: middle .fit[] --- class: middle ## Find the factorial of $n$ - $n! = n \times n-1 \times \ldots \times 2 \times 1$ - $n! = n \times (n-1)!$ - Special case: $0! = 1$ --- class: middle .fit[] --- class:middle,center ## Recursion ### A function calling itself --- class:middle,center # Types --- class:middle ### `1010010101010101001111010..` can mean - 1933091 - 34.95108 - `hello` - an image --- class:middle ### A variable needs a type to be interpreted correctly. --- class:middle ### A type is represented by a fixed, finite, number of bits. ### Different types can be represented by a different number of bits. --- class:middle, center ### 1 bit: `1` or `0` black or white<br> true or false<br> yes or no<br> S or U --- class:middle, center ### 2 bits: `11`, `10`, `01`, or `00` north, south, easy, west<br> spring, summer, fall, winter --- class:middle, center ### In general, $k$ bits can represent $2^k$ values --- class:middle, center ### more bits $\rightarrow$ more memory, but can represent bigger range ### fewer bits $\rightarrow$ less memory, but represent smaller range --- class:middle, center ### When writing programs for embedded systems, IoT devices, sensors, etc, you need to be frugal with memory usage. ### In CS1010, however, we will go with more bits for better precision. --- class:middle, center ## Integers --- class:middle, center ### 8 bits: 256 different integers 0 to 255 (for unsigned)<br> -128 to 127 (for signed) --- class:middle, center ### 64 bits signed -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 <br> to <br> 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 --- class:middle, center ## Characters --- class:middle, center ### 8 bits: 127 different symbols using ASCII standards ``` 0-9, A-Z, a-z <>?:”{}!@#$%^&* ()_+-=[]\';/., ``` return, tab, escape, etc --- class:middle, center ### up to 32 bits: Unicode (UTF-8) 11111011000000000 😀 --- class:middle, center ## Real numbers (also called floating point numbers) --- class:middle, center ### There are infinitely many real numbers but only a finite sequence of bits can only represent a finite set of real numbers. --- class:middle, center ### Not every real number can be presented precisely E.g., `0.1 + 0.2` is `0.30000000000000004` --- class:middle, center ### We normally use 32, 64, or 128 bits to represent real numbers. --- class:middle, center ### A variable needs a type to be interpreted correctly. --- class:middle, center set $total$ to $sum(L, k)$<br> set $avg$ to $mean(L, k)$ $k$ is an integer<br> $total$ is an integer<br> $avg$ must be a real number --- class: bottom .tiny[ Version: 1.1 Last Updated: Tue Aug 18 12:24:32 +08 2020 ]